
Shareholder equity can also be expressed as a company’s share capital and retained earnings less the value of treasury shares. Though both methods yield the exact figure, the use of total assets and total liabilities is more illustrative of a company’s financial health. As such, it helps the shareholders and investors make more informed decisions about their investments. Further, it also allows the analysts and other readers of the financial statements to understand what factors resulted in the change in the equity capital. A company’s balance sheet contains all of the information needed to calculate shareholders’ equity. A statement of shareholder’s equity is a report on the changes of value in equity and ownership interest in a company for the shareholder from the beginning to the end of an accounting year.

The Role of Retained Earnings in Increasing Stockholder Equity
Statement of stockholders’ equity is one of the five components of the financial statements. The beginning statement of shareholders equity example balance is needed to start and is obtained from the previous accounting periods ending equity balance to calculate the statement. Income and capital contributions are added to the beginning balance total, while business losses and owner draws are subtracted.
- Because of this, the statement of owner’s equity is often viewed as the connecting link between the income statement and balance sheet.
- Dividends reduce retained earnings as they represent a distribution of profits to shareholders.
- This affects the equity accounts by increasing common stock and additional paid-in capital.
- Rather than paying this income to shareholders, it remains with the company and is reinvested in the business.
- If the amount is high, it determines that the company has made quite an amount of retained earnings and is considered profitable.
Understanding the Variances: Accrued Expenses vs Accounts Payable

It is what are retained earnings the amount of money earned through a company’s income, but not yet dispatched to shareholders. If the amount is high, it determines that the company has made quite an amount of retained earnings and is considered profitable. The systematic allocation of the cost of an asset from the balance sheet to Depreciation Expense on the income statement over the useful life of the asset. (The depreciation journal entry includes a debit to Depreciation Expense and a credit to Accumulated Depreciation, a contra asset account).

Statement of Comprehensive Income
For an initial public offering, a company will sell a specific amount of stock for a specific price. There are a number of items included in the Statement of Stockholders’ Equity, and these will be explained below. However, once broken down, it is easier to understand it as simply the value a business adds through operations that remain with it. Understanding the interconnections between these statements is valuable for several reasons. Shareholders’ equity plays an intricate role in a company’s corporate social responsibility (CSR) and sustainability initiatives. There is also such a thing as negative brand equity, which is when people will pay more for a generic or store-brand product than they will for a particular brand name.
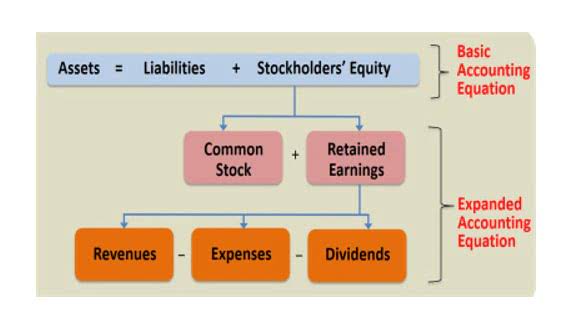
- Let’s understand it with the help of an example, if a company XYZ has $90,000 in total assets and $50,000 in liabilities, the stockholders’ equity will then be $40,000.
- Those stockholders are interested in receiving financial statements which report the results and financial position of the entire economic entity, which is all of the subsidiaries and the parent corporation.
- As a result of this, they are also often known as “paper” profits or losses.
- Companies may need to adjust their accounting practices to comply with new laws or standards, which can significantly alter their reported equity.
- It gives shareholders, investors and the company’s owner a true picture of how the business is performing and is usually measured monthly, quarterly or annually.
- This financial statement is needed because many investors and financial analysts believe that “cash is king” and cash amounts are required for various analyses.
Publicly-Traded Corporations

Under the indirect method, the first amount shown is the corporation’s net income (or net earnings) from the income statement. Assuming the net income was $100,000 it is listed first and is followed by many adjustments to convert the net income (computed under the accrual method of accounting) to the approximate amount of cash. The term comprehensive income consists of 1) a corporation’s net income (which is detailed on the corporation’s income statement), and 2) a few additional items which make up what is known as other comprehensive income.
In addition to US GAAP the external financial statements of a publicly-traded U.S. corporation must comply with the reporting requirements of the U.S. government agency, Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). Among the many required reports is the Annual Report to the SEC, Form 10-K. The notes (or footnote disclosures) are required by the full disclosure principle because the amounts and line descriptions on the face of the financial statements cannot provide sufficient information. In fact, there may be some large potential losses that cannot be expressed as a specific amount, but they are critical information for lenders, investors, and others.
- The statement of shareholders’ equity reports the changes in the value of shareholders’ equity from the beginning of an accounting period to the end of it.
- The amounts attributable to owners of the parent entity and the amounts attributable to the non-controlling interest have to be shown separately when statement of stockholder’s equity is to be made for a group of companies.
- It starts with the beginning balance, adds net income, and subtracts dividends.
- Now that we know what the purpose of this financial statement is, let’s analyze how this report is formatted in a little more detail.
- Stockholders’ equity is the company that has settled the value of assets available to the shareholders after all liabilities.
Net sales is the gross amount of Sales minus Sales Returns and Allowances, and Sales Discounts for the time interval indicated on the income statement. The balance sheet of the same corporation will have as its heading “Consolidated Balance Sheets” and will report the amounts as of the final instant as of Accounts Payable Management December 31, 2024 and the final instant as of December 31, 2023. The positive amounts in this section of the SCF indicate the cash inflows or proceeds from the sale of property, plant and equipment and/or other long-term assets.
- Additional paid-in capital includes the excess amount paid by investors over the par value of the stock, indicating the premium investors are willing to pay for the company’s equity.
- The good news is that the rules for the statement of changes in equity did not change, when compared to the older standard IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements.
- We research and recommend products and services suitable for various business types, investing thousands of hours each year in this process.
- The “statement of shareholders equity” is a financial document that outlines the changes in a company’s equity over a specific accounting period.
- Companies must carefully manage these changes to maintain investor confidence and ensure long-term stability.
When dividends are paid out, they are deducted from the company’s retained earnings and therefore reduce equity. At the end of its fiscal year 2024, Apple had an accumulated deficit of $19.2 billion. The company also reported an accumulated other comprehensive loss of $7.2 billion. The Statement Of Shareholder Equity shows the value of a company after investors and stockholders have been paid out. When combined with other metrics, shareholders’ equity can help you develop a holistic picture of the company and make sound investing decisions.
